
Dowd proposed a system of hourly standard time zones for North American railroads around 1863, although he published nothing on the matter at that time and did not consult railroad officials until 1869.
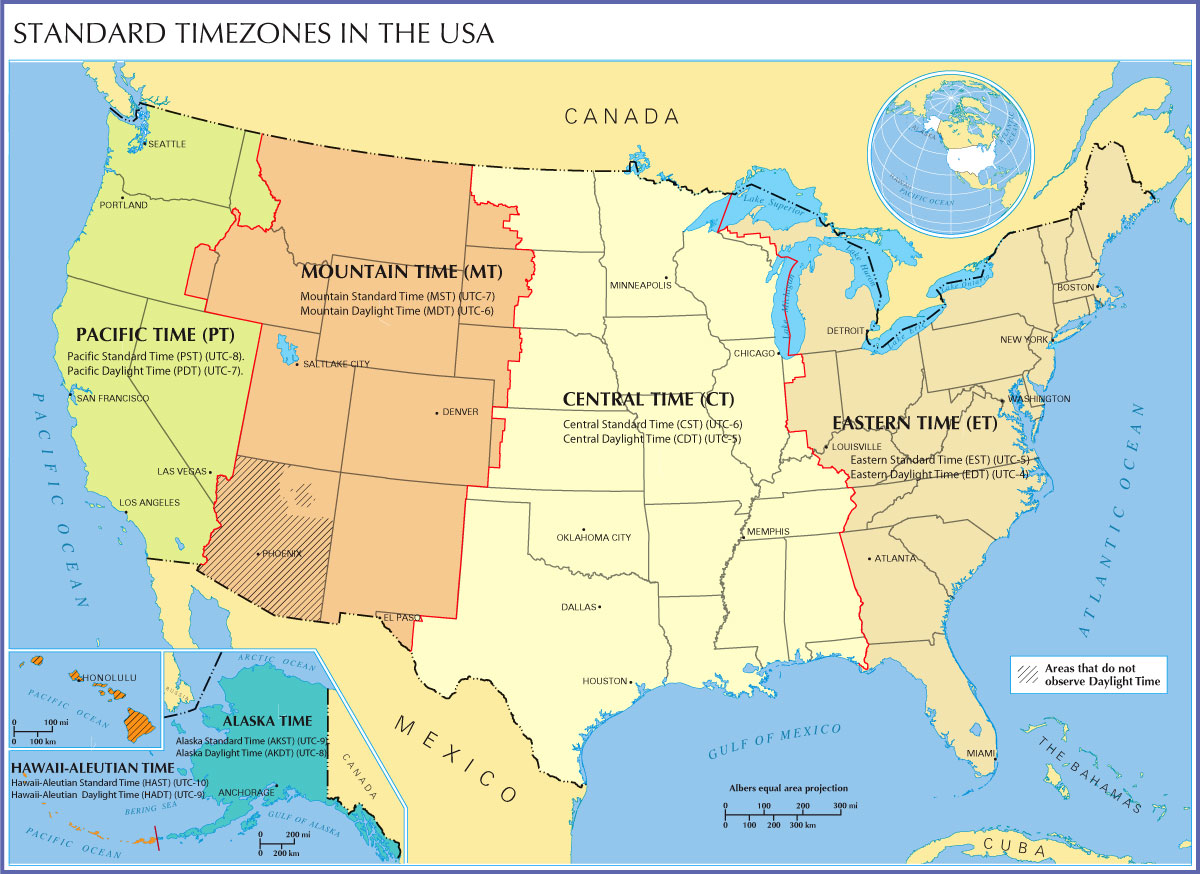
ġ913 time zone map of the United States, showing boundaries very different from todayĬharles F. Some junctions served by several railroads had a clock for each railroad, each showing a different time. Each railroad used its own standard time, usually based on the local time of its headquarters or most important terminus, and the railroad's train schedules were published using its own time. Timekeeping on North American railroads in the 19th century was complex. This standard was known as New Zealand Mean Time. It was based on longitude 172☃0′ east of Greenwich, that is 11 hours 30 minutes ahead of GMT. On November 2, 1868, the then British Colony of New Zealand officially adopted a standard time to be observed throughout the colony. Some British clocks from this period have two minute hands, one for the local time and one for GMT. By 1855, 98% of Great Britain's public clocks were using GMT, but it was not made the island's legal time until August 2, 1880. This practice was soon followed by other railway companies in Great Britain and became known as Railway Time.Īround August 23, 1852, time signals were first transmitted by telegraph from the Royal Observatory.
#DOES GOOGLE MAPS ACCOUNT FOR TIME ZONE CHANGES PORTABLE#
In November 1840, the Great Western Railway started using GMT kept by portable chronometers. In the 19th century, as transportation and telecommunications improved, it became increasingly inconvenient for each location to observe its own solar time. The control panel of the Time Zone Clock in front of Coventry Transport Museum


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
